Custom Silicone Printing Explained: Methods, Applications, and How to Choose the Right Process
Silicone printing methods play an important role in modern product branding, especially for OEM manufacturers and brands that require logos, graphics, or decorative elements on silicone products.
Unlike standard plastic printing, silicone printing requires specialized processes due to silicone’s flexibility, surface energy, and curing behavior.
This article explains what custom silicone printing is, the most common printing and decoration methods, and how manufacturers select the right process for stable mass production.

What Is Custom Silicone Printing?
Custom silicone printing refers to the application of logos, text, patterns, or decorative graphics onto silicone products using production-ready printing or molding techniques.
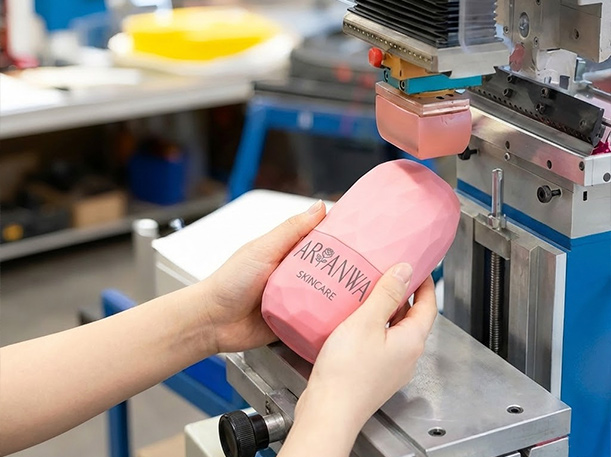

Because silicone is elastic, heat-resistant, and chemically stable, it cannot be printed using ordinary ink systems designed for plastics or metals. Each silicone printing method is developed to balance:
-
Adhesion stability
-
Visual clarity
-
Durability under real-world use
-
Production efficiency for OEM orders
As a result, custom silicone printing is not a one-size-fits-all process, but a set of methods selected based on product design and production requirements.
Common Silicone Printing and Logo Decoration Methods
1. Pad Printing on Silicone
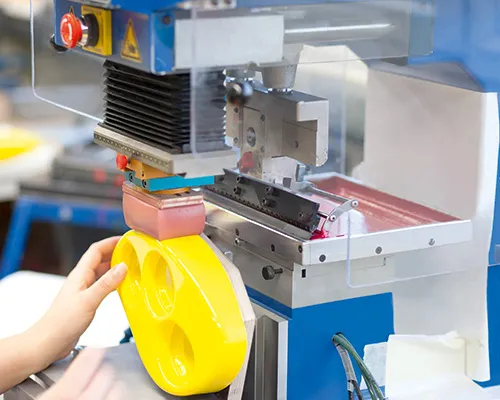

Pad printing is commonly used for applying logos or text to curved or irregular silicone surfaces.
A flexible silicone pad transfers ink from an etched plate onto the product surface, allowing precise placement even on non-flat geometry.
This method is widely used for:
-
Logos and text
-
Simple graphics
-
Medium to large OEM production runs
Pad printing offers good adhesion and repeatability, making it suitable for many functional silicone products.
2. Screen Printing on Silicone
Screen printing applies ink through a mesh screen directly onto the silicone surface.
It is best suited for flat or slightly curved silicone parts and designs with limited color counts.

Typical applications include:
-
One to three solid-color logos
-
Large-area markings
-
High-volume OEM production
Screen printing is valued for consistent ink thickness and strong visual contrast.
3. Silicone Digital Printing
Silicone digital printing applies full-color graphics directly onto the silicone surface without the need for printing plates or screens.
This method is ideal for:
-
Full-color or photo-style designs
-
Variable artwork
-
Short-run customization and promotional products
While digital printing provides excellent visual flexibility and fast setup, it is generally less abrasion-resistant than molded or IMD solutions.
4. In-Mold Decoration (IMD)
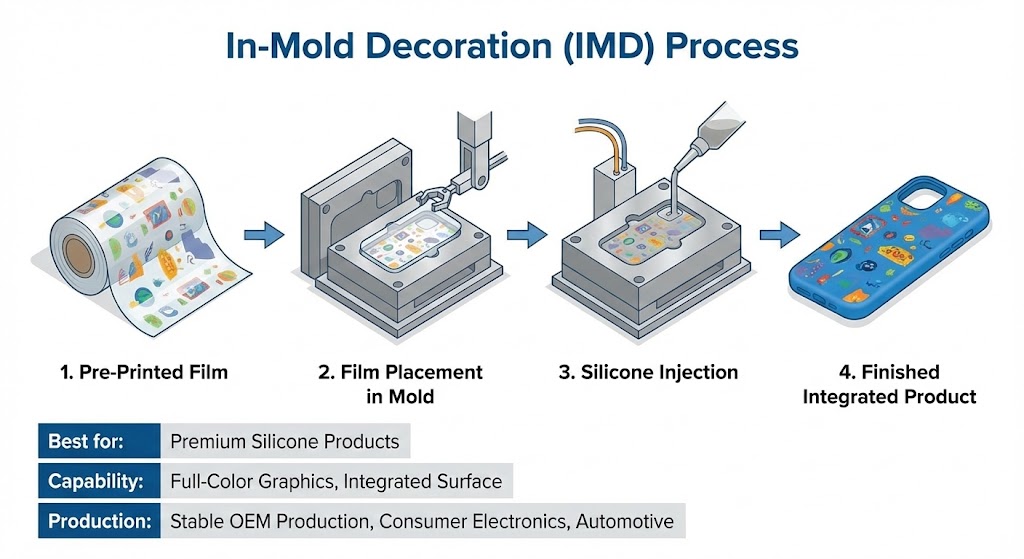
In-mold decoration integrates a pre-printed film directly into the silicone molding process.
The graphic becomes part of the finished product surface rather than a surface-applied layer.
IMD is commonly used for:
-
Premium silicone products
-
Full-color, high-definition graphics
-
Stable, long-term OEM production
Because the decoration is protected by the molded silicone layer, IMD offers excellent durability and surface consistency.
5. Heat Transfer Printing
Heat transfer printing uses pre-printed films that are transferred onto the silicone surface using heat and pressure.
This method supports:
-
Multi-color graphics
-
Decorative patterns
-
Short to medium OEM batches
Heat transfer printing is often selected when visual impact is prioritized over long-term abrasion resistance.
6. Water Transfer Printing
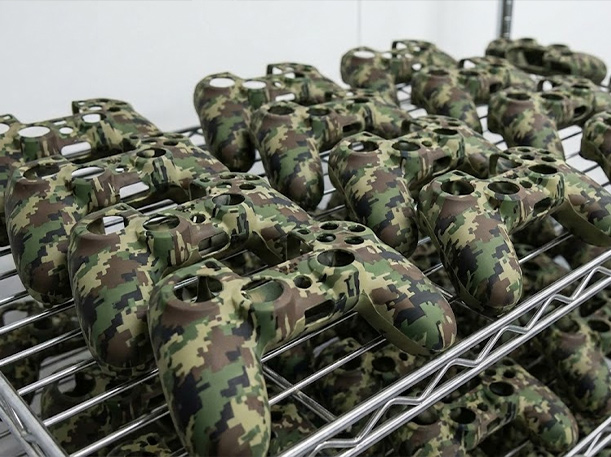

Water transfer printing (also known as hydro dipping) allows full-wrap decorative patterns to be applied to complex 3D silicone shapes.
It is commonly used for:
-
Camouflage, carbon fiber, or wood grain patterns
-
Irregular or highly contoured products
-
Small to medium production volumes
This process enables designs that are difficult to achieve with flat printing methods.
7. Embossed and Debossed Molded Logos
Instead of printing ink, embossed and debossed logos are formed directly in the silicone mold.
This approach provides:
-
Maximum durability
-
No ink fading or peeling
-
Long-term brand identification
Molded logos are often used for functional or outdoor silicone products where wear resistance is critical.
How Manufacturers Choose the Right Silicone Printing Method
Selecting the correct custom silicone printing method involves more than visual preference.
Manufacturers evaluate each project from an OEM production perspective, considering factors such as:
-
Silicone material type and surface texture
-
Logo size, color count, and placement
-
Expected usage environment and abrasion frequency
-
Required durability and visual performance
-
Production volume, tooling requirements, and cost targets
The final decision aims to deliver production-ready results, not just visually appealing samples.
Durability Considerations in Silicone Printing
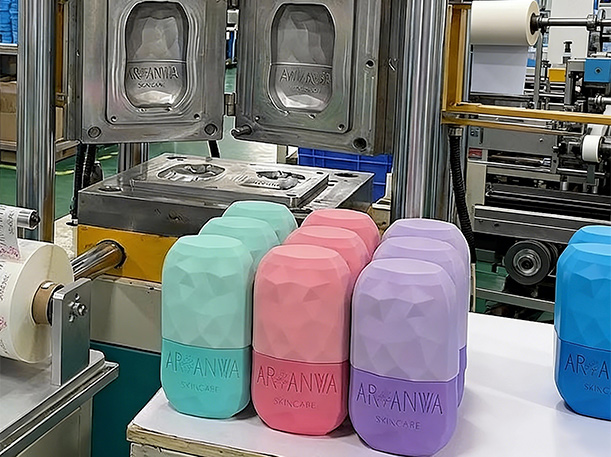

Different silicone printing methods offer different durability levels:
-
Molded embossed or debossed logos provide the highest wear resistance
-
IMD offers strong protection for full-color graphics
-
Pad and screen printing deliver reliable performance for most applications
-
Digital and transfer printing prioritize visual flexibility
Understanding how the product will be used is essential when selecting the appropriate method.
Applications of Custom Silicone Printing
Custom silicone printing is widely used across multiple industries, including:
-
Consumer electronics accessories
-
Promotional products
-
Kitchen and food-contact items
-
Medical and healthcare products
-
Industrial and outdoor equipment
Each application may require a different balance between appearance, durability, and production efficiency.
Conclusion
Custom silicone printing is a specialized manufacturing process that combines material science, printing technology, and production engineering.
By understanding the available methods and their strengths, brands and OEM buyers can make informed decisions that support long-term product performance and stable mass production.
Rather than choosing based solely on appearance, successful silicone printing projects are built on proper process selection, testing, and production planning.


